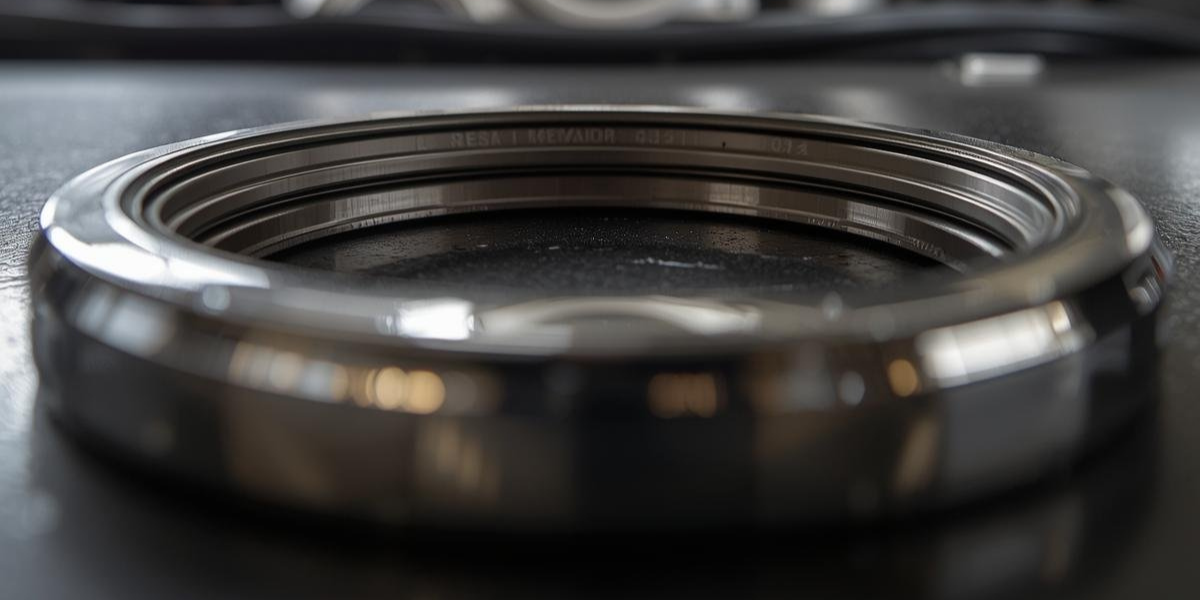

- Introduction to Oil Seals in Automotive Engineering
When it comes to the performance and reliability of an engine, every small component plays a critical role. Among these, oil seals stand out as unsung heroes that often go unnoticed by drivers, yet their importance cannot be overstated. Oil seals, also known as shaft seals or radial lip seals, are circular sealing devices designed to keep lubricants inside while preventing contaminants like dirt, dust, and moisture from entering. In vehicles, they are used in multiple systems such as the engine, gearbox, transmission, and wheel hubs. Without effective oil seals, engines would quickly lose lubrication, leading to friction, wear, overheating, and ultimately costly breakdowns. Understanding their function and importance helps drivers and mechanics alike appreciate how these small parts contribute significantly to the overall efficiency and lifespan of a vehicle.
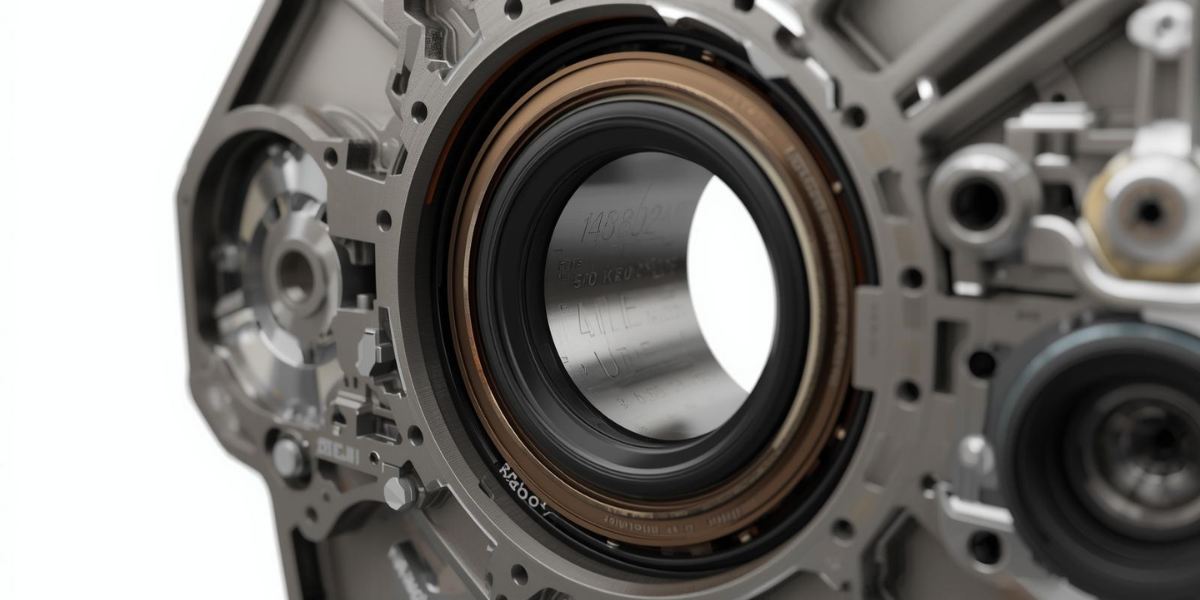

- How Oil Seals Work and Their Core Function
At their core, oil seals are engineered to perform two primary tasks: retaining essential lubricants inside mechanical systems and blocking harmful contaminants from getting in. They are typically made from durable materials like nitrile rubber, silicone, PTFE (Teflon), or Viton, combined with a metal case and a spring-loaded lip for a tighter fit. In an engine, the oil seal is placed around a rotating shaft — such as the crankshaft or camshaft — where it maintains a thin lubricating film that reduces friction while ensuring no oil escapes. This delicate balance allows moving parts to operate smoothly under high pressure and temperature conditions. Additionally, by preventing dirt and moisture from entering, oil seals protect the engine from internal corrosion and mechanical damage. Their simple yet effective design is a testament to how crucial even the smallest components are in the seamless operation of modern vehicles.

- Importance of Oil Seals in Engine Performance
A well-functioning oil seal directly impacts engine performance in multiple ways. First, it maintains proper lubrication levels, which reduces wear and tear on vital components such as bearings, pistons, and shafts. Second, it minimizes oil leakage, ensuring that the engine operates with the correct oil pressure, which is necessary for efficient combustion and power delivery. Third, it helps regulate engine temperature since oil also acts as a coolant by carrying heat away from moving parts. Furthermore, faulty oil seals can lead to visible oil leaks under the vehicle, which not only reduces performance but also poses environmental hazards and fire risks. Drivers often underestimate the significance of oil seals until problems arise, but regular maintenance and timely replacement can prevent engine inefficiencies, unexpected repairs, and costly breakdowns. In short, oil seals are vital for keeping an engine running smoothly, efficiently, and reliably.
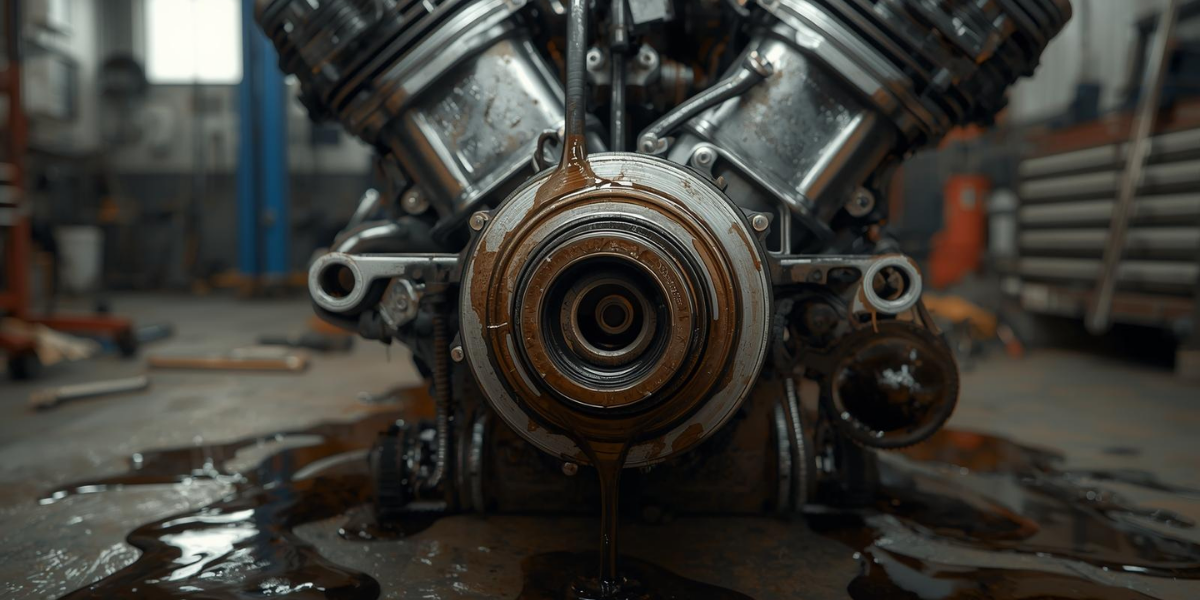
- Common Problems with Oil Seals and Their Symptoms
Like all mechanical components, oil seals are prone to wear and failure over time. High engine temperatures, constant friction, poor lubrication quality, and exposure to contaminants can cause seals to crack, harden, or lose their elasticity. When this happens, symptoms often appear in the form of oil spots under the car, blue exhaust smoke from burning oil, or unusual noises coming from the engine or gearbox. Another clear indicator is a noticeable drop in oil levels despite regular refilling. If ignored, damaged oil seals can result in severe engine problems, including bearing failure, overheating, or even complete engine seizure. Regular inspection during routine maintenance can help identify oil seal issues early. Mechanics usually check areas around the crankshaft, camshaft, and differential for leaks, ensuring faulty seals are replaced before they compromise overall engine health.
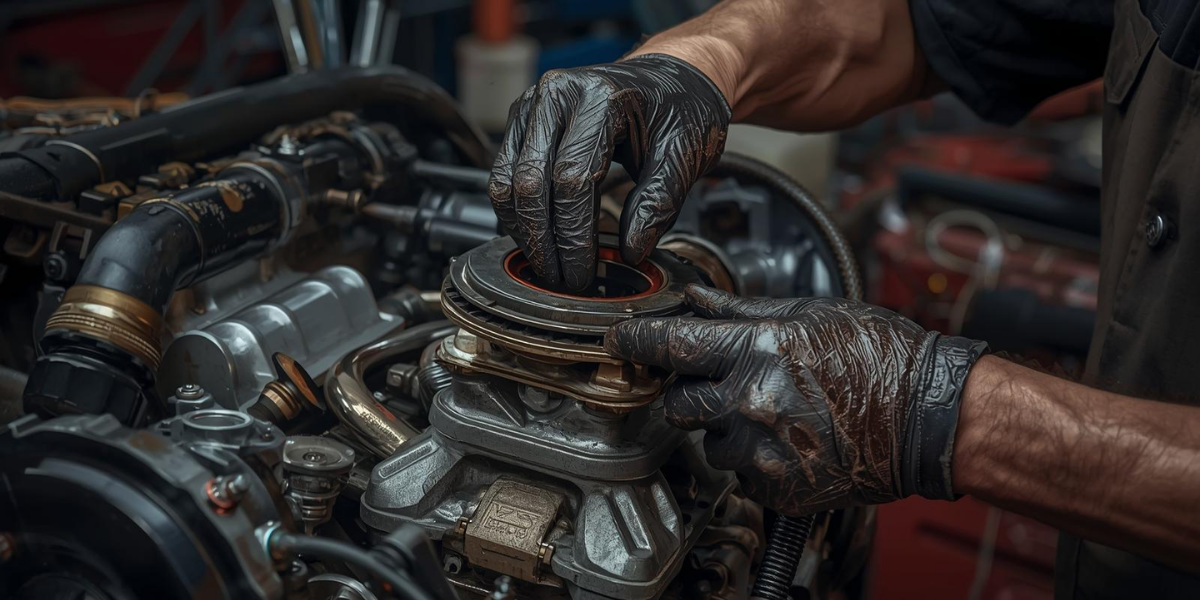

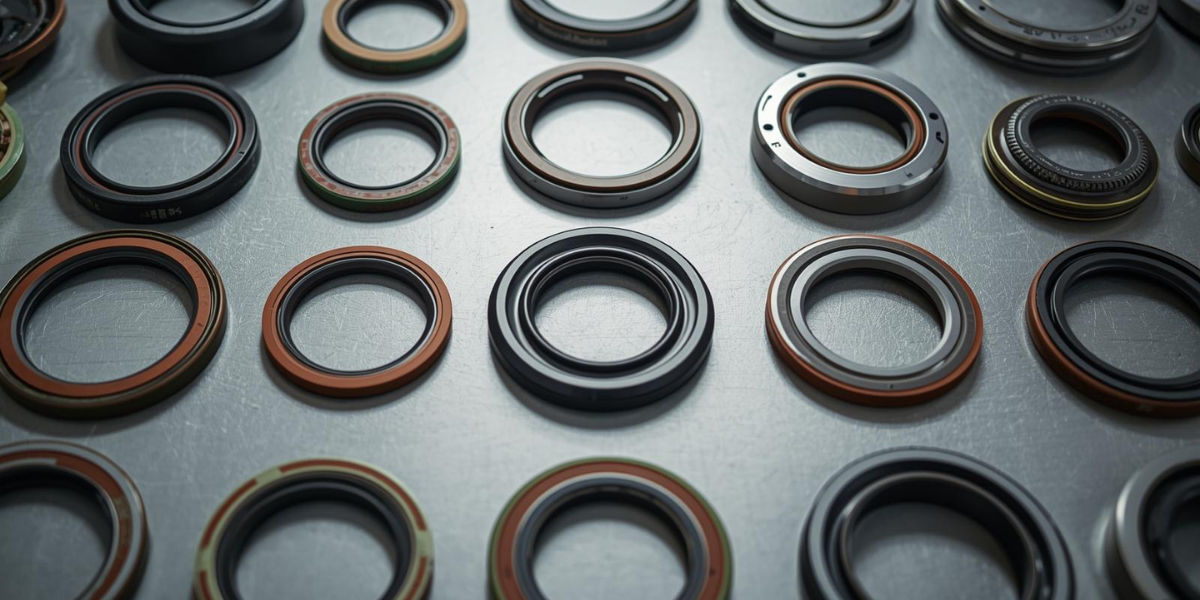
- Different Types of Oil Seals and Their Applications
Oil seals are not one-size-fits-all components; they come in various designs tailored to different automotive applications. The most common type is the radial lip seal, which is used in engines and transmissions to seal rotating shafts. Hydraulic oil seals are designed for high-pressure environments found in steering systems and hydraulic machinery. Valve stem seals, another variant, regulate oil flow to the engine’s valve stems, preventing excess oil consumption and smoke emissions. Wheel hub seals are critical for keeping lubricants in wheel bearings while blocking dirt and water from entering. Additionally, industrial-grade oil seals are used in heavy-duty vehicles, where they withstand extreme conditions and prolonged use. By choosing the right type of oil seal for the application, mechanics ensure that engines and systems remain leak-free, efficient, and durable under all operating conditions.

- Maintenance Tips and Final Thoughts on Oil Seals
Although oil seals are small and inexpensive, their impact on engine performance is significant. To maximize their lifespan, regular engine maintenance is essential. This includes using high-quality lubricants, ensuring oil changes are performed on schedule, and inspecting seals for wear during routine servicing. When replacement is necessary, it’s always best to use high-quality OEM or branded seals that match the specifications of the vehicle. Installing low-quality or ill-fitted seals may save money upfront but can lead to premature failure and higher repair costs in the long run. Drivers should also pay attention to early warning signs like leaks or smoke, as these often indicate a seal problem. Ultimately, oil seals are vital for maintaining efficiency, reducing wear, preventing leaks, and ensuring long-term engine reliability. By giving attention to these often-overlooked parts, car owners can enjoy smoother rides, better fuel efficiency, and extended vehicle life.